Learn About Tobacco Farming in the Philippines
Introduction
Tobacco farming in the Philippines has deep roots, interwoven with the country’s history and agricultural landscape. Over the years, this industry has grown, adapted, and thrived, thanks to the hard work of tobacco farmers and favorable growing conditions. With its unique blend of culture, tradition, and opportunity, farming tobacco in the Philippines is more than just a livelihood—it’s a way of life.
Transitioning from a casual interest to a full-blown farming venture might seem daunting at first. But here, we’ll guide you through the ins and outs of why growing tobacco can be both rewarding and lucrative. By the end, you’ll see that the journey from seed to harvest is filled with possibilities and potential.
To learn more about the history, importance, and economic impact of the tobacco industry in the Philippines, check out the official Wikipedia page on tobacco production in the country.
Why You Should Farm Tobacco in the Philippines
If you’re considering agriculture as a source of income, tobacco farming in the Philippines stands out as a compelling choice. The country’s tropical climate, rich soil, and long history of tobacco cultivation create the perfect environment for this crop. But it’s not just about ideal conditions; it’s about tapping into an established and ever-growing market.
Can You Make Good Money Farming Tobacco Plants? Absolutely! Many Filipino farmers have found financial success through tobacco farming. While it’s not a get-rich-quick scheme, the combination of dedication, proper management, and leveraging government or industry support can yield impressive profits. The demand for high-quality tobacco, both locally and internationally, ensures that there’s always a market for well-cultivated crops.

What do I need to know about farming tobacco in the Philippines?
Farming tobacco in the Philippines requires an understanding of the local agricultural practices, climate, and market demands. Below are key considerations:
1. Climate and Soil Requirements
- Climate: Tobacco grows well in tropical climates with distinct dry and wet seasons. The Philippines’ climate is generally suitable, especially in regions like Ilocos, Cagayan Valley, and Mindoro.
- Soil: The crop thrives in well-drained, fertile loam or sandy soil with a pH of 5.5 to 6.5. Testing soil quality and ensuring proper preparation are crucial.
2. Varieties of Tobacco
- The Philippines grows several types of tobacco, including:
- Virginia tobacco: Used for cigarettes.
- Burley tobacco: Commonly used in blends.
- Native tobacco: Used locally for cigars and traditional consumption.
- Choose a variety based on your region’s conditions and market demand.
3. Planting and Cultivation
- Seedbeds: Start with high-quality seeds in seedbeds before transplanting.
- Planting season: Typically starts during the dry season to avoid excessive rain, which can harm the crop.
- Crop rotation: Avoid planting tobacco consecutively on the same plot to prevent soil depletion and diseases.
4. Water and Fertilization
- Irrigation: Tobacco needs consistent but moderate watering, especially during the early stages.
- Fertilization: Use balanced fertilizers rich in nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Organic fertilizers or compost can also be beneficial. Potasium Nitrate is a great fertilizer to use for tobacco plants as detailed here.
5. Pest and Disease Management
- Common pests include aphids, tobacco worms, and whiteflies.
- Diseases such as black shank, mosaic virus, and root rot are common threats.
- Employ integrated pest management (IPM) techniques, including crop rotation, resistant varieties, and biological controls.
6. Harvesting and Curing
- Harvesting: Leaves are harvested in stages as they ripen, starting from the bottom.
- Curing: Proper curing is essential to develop the desired aroma and quality. This can involve air curing, flue curing, or sun curing, depending on the variety.
7. Government Regulations
- The Philippine government regulates tobacco farming through agencies like the National Tobacco Administration (NTA).
- Farmers may need to register with the NTA and comply with guidelines on production, sale, and quality standards.
8. Market and Economics
- Tobacco farming can be profitable but is heavily influenced by market prices, which fluctuate based on demand.
- Selling options include cooperatives, direct buyers, or government-supported programs.
- Diversification is advisable to mitigate risks associated with price volatility.
9. Health and Ethical Considerations
- Tobacco farming is labor-intensive and may pose health risks due to exposure to pesticides and nicotine.
- Ethical concerns about promoting tobacco consumption should be considered, especially as the industry faces global scrutiny.
10. Support and Resources
- The NTA and local agricultural offices provide training, financial support, and technical assistance.
- Joining a cooperative or association can help access resources and better pricing.
Understanding these factors and staying updated on industry trends can help ensure success in tobacco farming in the Philippines.

How Much Land Area Do I Need To Make A Significant Income from Tobacco?

What’s the Best Region to Grow Tobacco in the Philippines?
The best regions to grow tobacco in the Philippines are those with suitable climate, soil, and established infrastructure for tobacco farming. These include:
1. Ilocos Region (Region I)
- Provinces: Ilocos Norte, Ilocos Sur, La Union, Pangasinan.
- Why it’s ideal:
- Known as the “Tobacco Capital of the Philippines.”
- Favorable climate with a distinct dry season ideal for curing tobacco.
- Well-drained sandy loam soil perfect for growing Virginia and native tobacco.
- Established market and support infrastructure through the National Tobacco Administration (NTA).
2. Cagayan Valley (Region II)
- Provinces: Cagayan, Isabela, Nueva Vizcaya, Quirino.
- Why it’s ideal:
- Suitable for Virginia and Burley tobacco varieties.
- Fertile alluvial plains and river valleys conducive to high yields.
- Consistent rainfall patterns support growth during critical stages.
3. Central Luzon (Region III)
- Provinces: Tarlac, Nueva Ecija, Pampanga.
- Why it’s ideal:
- Known for producing Burley tobacco.
- Accessible markets and infrastructure for drying and processing.
- Farmers often rotate crops like rice and corn with tobacco for sustainable practices.
4. Occidental Mindoro
- Why it’s ideal:
- Known for producing high-quality Virginia tobacco.
- Good climate and soil conditions for commercial-scale production.
- Strategic location for export due to proximity to ports.
Factors to Consider:
- Climate: Ensure the region has a defined dry season for optimal curing and reduced risk of leaf damage from excessive rainfall.
- Soil: Test soil for fertility and drainage capabilities. Regions with sandy loam or well-drained alluvial soil are preferred.
- Infrastructure: Choose areas with established curing facilities, access to markets, and technical support from agencies like the NTA.
- Labor Availability: Tobacco farming is labor-intensive, so regions with sufficient skilled labor are advantageous.
For the best results, Ilocos Norte and Ilocos Sur are often considered the most optimal due to their long history, expertise, and infrastructure in tobacco production.

Is it easy to grow tobacco plants?

How Fast Does Tobacco Grow?
Tobacco plants grow relatively quickly, typically taking around 90 to 130 days from transplanting to reach maturity, depending on the variety and growing conditions. Here’s a breakdown of the growth stages and timeline:
1. Germination and Seedling Stage
- Timeline: 7 to 14 days
- Process:
- Seeds are sown in seedbeds and germinate within 7 to 10 days under optimal conditions.
- Seedlings grow in the nursery for 6 to 8 weeks before being transplanted.
- Key Factors:
- Requires moist, well-drained soil and warm temperatures (20–30°C).
- Protect seedlings from pests and diseases.
2. Transplanting
- Timeline: After 6–8 weeks in the seedbed.
- Process:
- Seedlings are moved to the field when they are 15–20 cm tall with a strong root system.
- Key Factors:
- Plant spacing is typically 45–60 cm apart to allow proper growth.
3. Vegetative Growth Stage
- Timeline: 50 to 70 days after transplanting.
- Process:
- Plants develop leaves rapidly, with larger leaves appearing during this stage.
- Growth depends on sunlight, water, and nutrients.
- Key Factors:
- Adequate irrigation, fertilization, and pest control are essential.
- Topping (removing flower buds) is often done to enhance leaf quality and size.
4. Maturity and Harvesting
- Timeline: 90 to 130 days after transplanting.
- Process:
- Leaves are harvested in stages as they mature, starting with the lower leaves.
- Ripeness is determined by leaf color, thickness, and texture.
- Key Factors:
- Proper timing ensures high-quality leaves for curing.
5. Curing (Post-Harvest)
- While not part of the growth cycle, curing takes an additional 1–2 months and is crucial for developing the desired aroma, color, and texture.
Factors That Influence Growth Speed:
- Variety:
- Virginia and Burley tobacco varieties may have slightly different growth rates.
- Climate:
- Warm, consistent temperatures promote faster growth.
- Excessive rain or cold can slow development.
- Soil and Nutrients:
- Fertile, well-drained soil and balanced fertilization accelerate growth.
- Management Practices:
- Proper spacing, irrigation, and pest control contribute to healthy, fast growth.
Summary
From sowing seeds to harvest, tobacco takes about 3 to 4 months to grow under optimal conditions. Adding the curing process extends the timeline to about 4 to 6 months from start to finish.

Do I need fertilizers to grow tobacco?
Yes, fertilizers are essential for growing healthy tobacco plants, as they help ensure the plants receive the nutrients needed for optimal growth and high-quality leaves. Tobacco is a nutrient-demanding crop and can deplete soil fertility quickly if nutrients are not replenished. Here’s what you need to know:
Key Nutrients for Tobacco Growth
- Nitrogen (N):
- Promotes vigorous leaf growth and dark green coloration.
- Too much nitrogen can result in overly thick leaves and delayed maturity, which may negatively affect leaf quality.
- Phosphorus (P):
- Encourages strong root development and overall plant vigor.
- Especially important during the seedling and early growth stages.
- Potassium (K):
- Enhances leaf quality, elasticity, and burning properties.
- Helps plants resist diseases and environmental stress.
- Calcium (Ca) and Magnesium (Mg):
- Support healthy cell walls and chlorophyll production.
- Deficiencies can cause issues like leaf spots or weak growth.
- Micronutrients (e.g., Zinc, Boron, Copper):
- Required in small amounts but critical for proper growth and development.
Types of Fertilizers for Tobacco
- Organic Fertilizers:
- Compost, manure, and other organic amendments can improve soil structure and fertility.
- Provide a slow, steady release of nutrients.
- Chemical Fertilizers:
- Specific blends are often designed for tobacco farming, typically labeled as NPK fertilizers (e.g., 8-14-24 or 12-12-18 ratios).
- Use these for precise nutrient management based on soil test results.
How to Apply Fertilizers
- Before Planting:
- Conduct a soil test to determine existing nutrient levels.
- Apply basal fertilizer (usually phosphorus and potassium) during field preparation.
- After Transplanting:
- Apply a nitrogen-rich fertilizer once the plants have established.
- Side-dress fertilizers near the plant base for efficient uptake.
- During Growth:
- Use potassium-heavy fertilizers during the later stages to enhance leaf quality.
- Avoid over-fertilizing, as it can lead to excessive leaf growth or nutrient imbalances.
Signs of Nutrient Deficiencies
- Nitrogen Deficiency: Pale yellow leaves and stunted growth.
- Phosphorus Deficiency: Dark green leaves with purple discoloration on veins.
- Potassium Deficiency: Browning or scorching along leaf edges (leaf tip burn).
- Calcium/Magnesium Deficiency: Curling leaves or chlorosis (yellowing) between veins.
Sustainable Practices
- Rotate crops to prevent soil depletion.
- Incorporate organic matter to enhance soil health.
- Use fertilizers judiciously to avoid environmental issues like runoff.
Summary
Fertilizers are crucial for growing high-quality tobacco, but their type and application should be tailored to the specific needs of your soil, region, and tobacco variety. A soil test is highly recommended to guide your fertilizer choices for maximum productivity and sustainability.
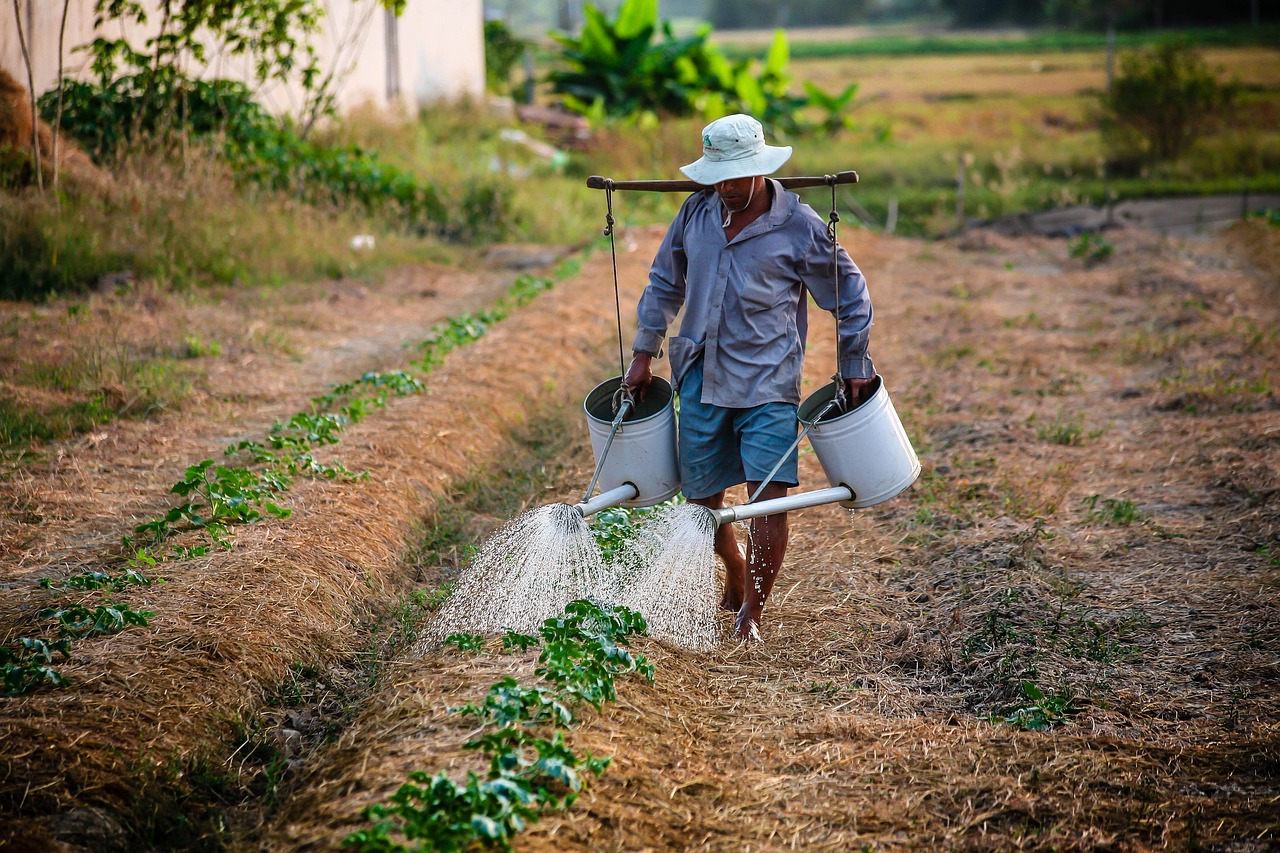

How Often do I Water Tobacco Plants in the Philippines?
Watering tobacco in the Philippines requires careful management, as both overwatering and underwatering can negatively affect plant growth and leaf quality. Here’s how you can manage watering effectively:
General Guidelines
- Water Needs:
- Tobacco plants require about 25–35 mm of water per week during their active growth stages.
- This translates to approximately 2.5–3.5 liters per square meter of planted area per week.
- Frequency:
- In areas with consistent rainfall during the wet season, additional watering may not be necessary.
- During the dry season, irrigation should be done 2–3 times per week, depending on soil type and evaporation rates.
Growth Stage-Specific Watering
- Seedling Stage (Nursery):
- Keep the soil moist but not waterlogged.
- Water lightly and frequently (1–2 times daily) to support germination and root development.
- Post-Transplanting Stage:
- Water immediately after transplanting to help the seedlings establish.
- Continue watering every 2–3 days for the first 1–2 weeks.
- Vegetative Growth Stage:
- Maintain consistent soil moisture, especially during the active leaf development phase.
- Water deeply once or twice a week if there is no rainfall.
- Maturity and Pre-Harvest Stage:
- Gradually reduce watering as the plants mature.
- Excess moisture during this stage can lead to poor curing quality and diseases like leaf rot.
Factors That Influence Watering Frequency
- Soil Type:
- Sandy Soil: Drains quickly and may require more frequent watering.
- Clay or Loam Soil: Retains moisture better, so watering can be less frequent.
- Weather Conditions:
- During the dry season, increase irrigation frequency to prevent drought stress.
- Monitor for heavy rains during the wet season to avoid waterlogging.
- Plant Health:
- Stressed or wilting plants may indicate the need for more water.
- Be cautious not to overwater, as tobacco roots are sensitive to standing water.
Irrigation Methods
- Drip Irrigation:
- Delivers water directly to the plant roots and minimizes evaporation.
- Ideal for conserving water and ensuring consistent moisture.
- Furrow Irrigation:
- Commonly used for larger fields; water is channeled between rows of plants.
- Ensure proper drainage to avoid waterlogging.
- Manual Watering:
- Suitable for small-scale operations or during the nursery stage.
Signs of Water Stress
- Underwatering:
- Wilting or drooping leaves, slower growth, and dry, brittle leaves.
- Overwatering:
- Yellowing leaves, root rot, and stunted growth.
Summary
In the Philippines, the frequency of watering tobacco depends on the season, soil type, and growth stage. During the dry season, water tobacco 2–3 times a week, while in the wet season, rainfall may suffice. Proper water management is crucial to producing high-quality leaves and maintaining healthy plants.
Quick FAQ on Farming Tobacco Plants
Q: Is tobacco farming lucrative? A: Yes, tobacco farming can be highly lucrative when done correctly. With proper knowledge and resources, farmers can achieve significant financial returns.
Q: Why farm tobacco in the Philippines? A: The Philippines offers ideal growing conditions, a strong market, and a rich tradition of tobacco farming, making it an excellent choice for cultivating this crop.
Q: How much money do I need to start growing tobacco? A: The initial investment depends on the scale of your farm, but it typically includes costs for seeds, equipment, labor, and maintenance. Small-scale operations can start with a modest budget.
Q: Can the Philippine government provide grants for tobacco farmers? A: Yes, there are programs and grants available to support tobacco farmers, including subsidies and training opportunities.
Q: What are the best places to farm tobacco in the Philippines? A: Regions like Ilocos and Cagayan are renowned for their favorable conditions for tobacco cultivation.
Final Words on Tobacco Farming in the Philippines
Filipino farmers are increasingly recognizing the potential of tobacco farming as a profitable venture. With the right approach, resources, and determination, growing tobacco in the Philippines is more than just worthwhile—it’s a gateway to sustainable income and agricultural innovation. Whether you’re new to farming or looking to diversify, the opportunities are endless. So why wait? Dive into the world of tobacco farming and unlock its potential today.
If you need more extensive information on farming tobacco plants in the Philippines, visit the National Tobacco Administration (NTA). They offer guidance, resources, and a detailed production manual to help you establish and manage a successful tobacco farm. The production manual can be viewed here.